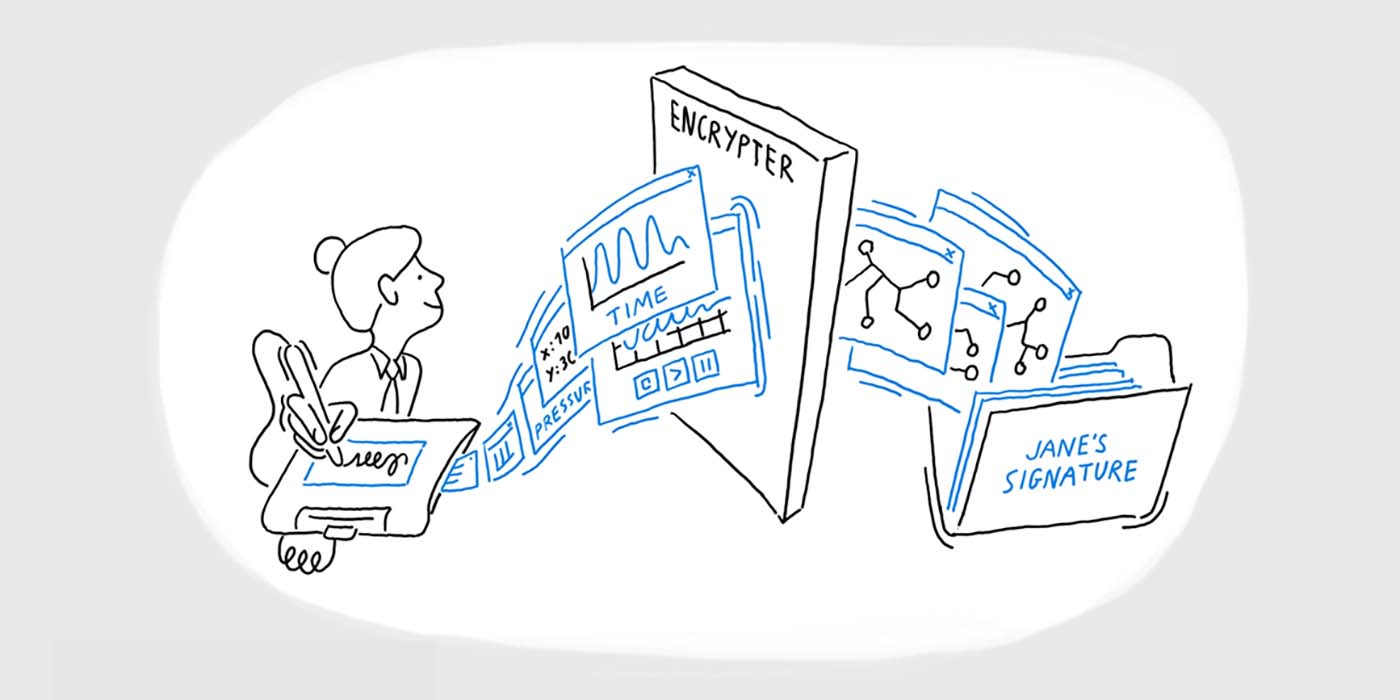
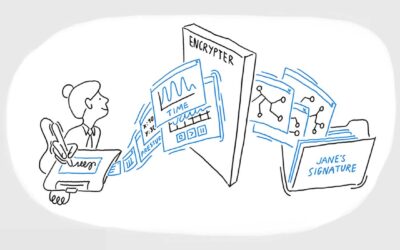
At this point, almost everyone has used an electronic signature before, even if it’s only to leave a rushed “John Hancock” after using a credit card at your local coffee shop. From everyday transactions to some of the most important documents you’ll ever sign, like a contract or a loan agreement, can be mediated through a signature on a signature pad, EMR display, or another digital signature device. So with that in mind, let’s take a moment to delve into the basics of a biometric electronic signature verification.
What is Biometric Electronic Signature Verification?
Electronic signature verification is the process of confirming that an electronic or digitally-captured signature is valid, legally binding, and has not been altered or added without consent of the signer. This means that you must check the identity of the signatory and ensure that the signature was created using methods that comply with legal and industry standards. To do this, it is important to be using software or a hardware device (or both) that can capture authentic and verifiable biometric data from a signature, including aspects like pen pressure sensitivity, length of time to sign, and number of strokes.
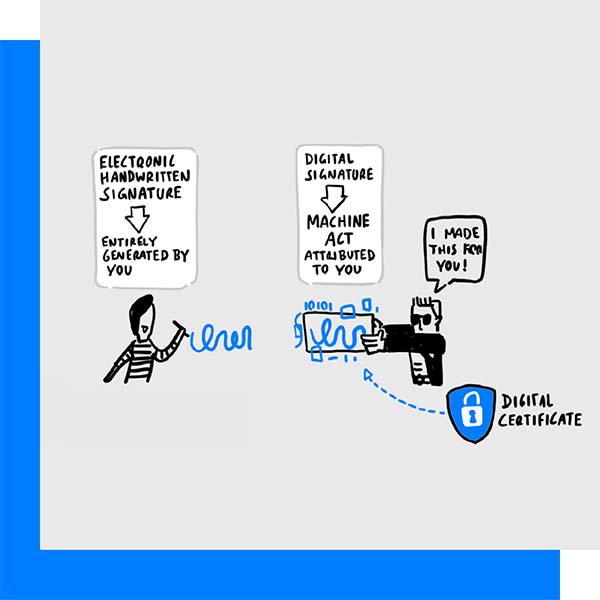
The verification process should typically include:
Authentication: Verifying the identity of the signer before they create an electronic signature. This can be achieved through various means such as passwords, email verification, or advanced methods like biometrics. For instance, electromagnetic resonance (EMR) tablets often use the sensitivity of their pen and surface to capture unique biometric data, ensuring the signer’s identity.
Integrity: It’s important to ensure that the document remains unedited and undisturbed following a signing ceremony. This is best accomplished by using biometrics and cryptographic techniques that create a unique imprint of the document, which changes and is noted if the document is modified.
Non-repudiation: The non-repudiation process includes being able to provide evidence that confirms the origin and integrity of the signed document, preventing the signer from denying their signature. Digital certificates and audit trails are often used as part of this investigative process.

Why is Electronic Signature Verification Important?
Verification enhances security by ensuring only authorized individuals can sign documents. It builds trust among parties in digital transactions, as they can be confident that the signatures are genuine and the documents have not been altered. According to a recent report, the digital signature market is expected to grow from $2.8 billion in 2020 to $14.1 billion by 2026, which only further emphasizes the increasing importance of secure digital signature solutions as the market expands and diversifies.
By now, most nations have regulations governing the use of electronic signatures, such as the eIDAS Regulation in the European Union and the ESIGN Act, which became law in the United States back in 2000. Verification ensures e-signatures comply with these laws, making them legally binding and enforceable. For example, the ESIGN Act grants electronic and digitally-captured signatures the same legal status as traditional signatures.
By eliminating the need for physical signatures and manual verification, electronic signature verification speeds up transactions and reduces costs associated with printing, mailing, and storing paper documents.
Richer verification mechanisms help prevent and minimize fraud by making it harder for unauthorized forgers to alter electronic signatures. This is crucial in sectors like finance, healthcare, and the public sector, where security is vital to the individual and the organization.
Finally, digital signatures reduce reliance on resource-intensive paper, which can help to contribute to environmental sustainability.
At Wacom, we know a lot about electronic signatures — it’s one of the places where we’ve innovated in digital pen and ink technology. We’d like to share some resources with you. Take a look at this link for more information.